Digital Twin
What is Digital twin?
A digital twin is a digital representation of a physical object, process, service, or environment that behaves and looks like its counterpart in the real world. A digital twin is, in essence, a computer program that uses real-world data to create simulations that can predict how a product or process will perform. These programs can integrate the IoT, AI, and software analytics to enhance the output or optimize performance. With the advancement of machine learning and factors such as big data, these virtual models have become a staple in modern engineering to drive innovation and improve performance. Creating Digital twins can allow the enhancement of strategic technology trends, prevent costly failures in physical objects, and also, by using advanced analytical, monitoring, and predictive capabilities, test processes and services. Graph Data plays critical roles in constructing virtual models, building cyber-physical connections, and executing intelligent operations using RDF. A digital twin can be a digital replica of an object in the physical world, such as machinery, a jet engine, or wind farms, or even larger items such as manufacturing plants, or even the smallest items like Drugs, or process or engineering systems, alternatively digital twin technology can be used to replicate processes in order to collect data to predict how they will perform.
How Digital works?
The life of a digital twin begins with Knowledge experts in industry, process, system, applied mathematics, or data science researching the physics and operational data of a physical object or system in order to develop a mathematical model that simulates the real-world original in digital space. Expertise or Specialists create digital twins to ensure that the virtual computer model can receive feedback from sensors, Experts & Systems that gather data from the real-world version. This allows the twin to simulate the physical object in real-time, in the process offering insights into performance and potential problems. A digital twin can be as complex or as simple as you require, with differing amounts of data determining how precisely the model simulates the real-world physical version. The twin can be used with a prototype to offer feedback on the product as it is developed or can even act as a prototype in its own right to model what could occur with a physical version when built.
Types of Digital twin?
Based on specific industries Twins are developed, but again it depends on complexity drivers, below are a few which help you examples of understanding
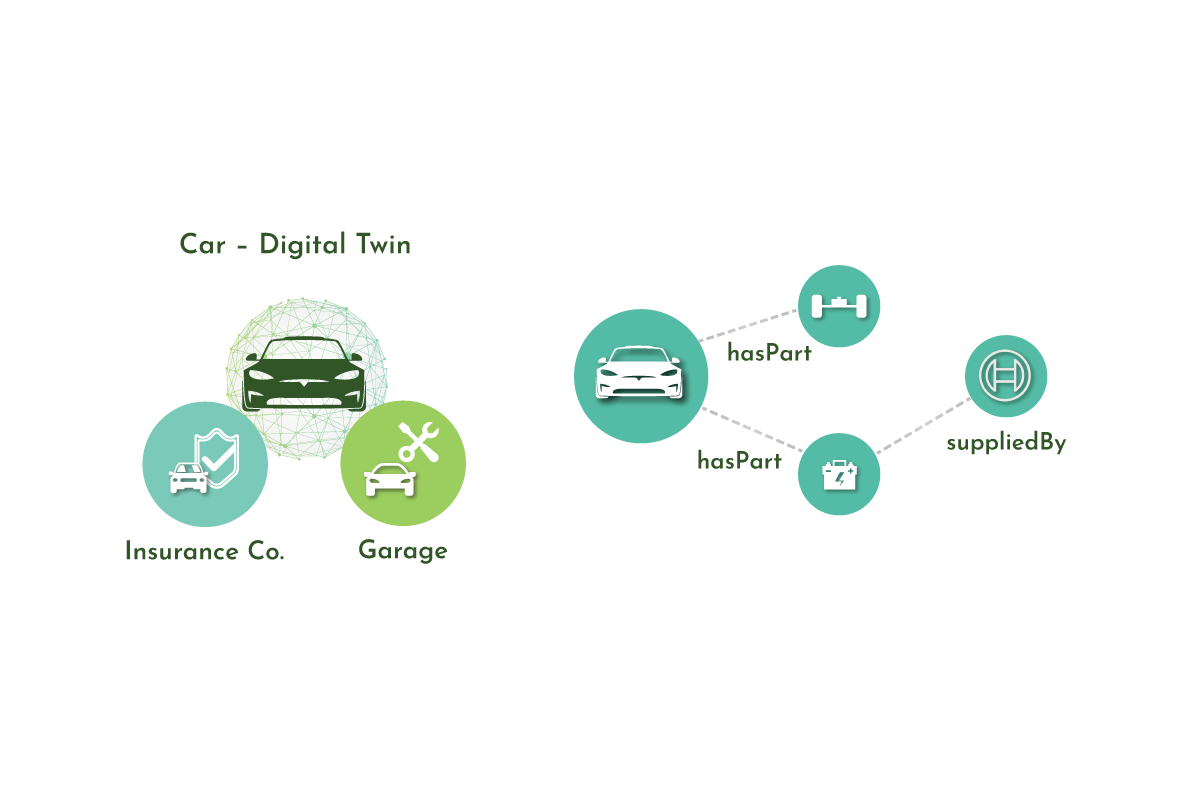
Components or Parts Twin- To simulate the smallest example of a functioning component.
Asset twins To simulate two or more components working together and let you study the interactions between them
System or unit twins Helps,let you see how multiple systems assets work together, simulating an entire production line (example0)
Process twins will help to see the absolute top-level view of systems working together, letting you figure out how an entire factory might operate.
Why Digital Twin?
Digital twins offer a variety of uses including logistics planning, product development and re-design, quality control/management, and systems planning. A digital twin can be used to save time and money whenever a product or process needs to be tested, whether in design, implementation, monitoring, or improvement. As mentioned above, digital twins can be created for a wide range of applications, for example, to test a prototype or design, assess how a product or process will work under different conditions, and determine and monitor lifecycles. A digital twin design is made by gathering data and creating computational models to test it. This can include an interface between the digital model and an actual physical object to send and receive feedback and data in real-time type of process can be used likely ; Digital Twin Prototype (DTP) - This is undertaken before a physical product is created Digital Twin Instance (DTI) – This is done once a product is manufactured in order to run tests on different usage scenarios Digital Twin Aggregate (DTA) – This gathers DTI information to determine the capabilities of a product, run prognostics and test operating parameters.
How we design & Develop Digital Twin?
Graph data & Knoledge Graphs
A digital twin requires Graph data & knowledge about an object or process in order for a virtual model to be created that can represent the behaviors or states of the real-world item or procedure. This data may relate to the lifecycle of a product and include design specifications, production processes, or engineering information. It can also include production information including equipment, materials, parts, methods, and quality control. Data can also be related to the operation, such as real-time feedback, historical analysis, and maintenance records. Other data used in digital twin design can include business data or end-of-life procedures. Once data is put across the graph database then knowledge is fused with data to build an exact replica of the physical twin.
Graph modelling & Ontologies
Once the data has been gathered using knowledge graphs, it can be used to create computational analytical models to show operating effects, predict states such as fatigue, and determine behaviors. These models can prescribe actions based on engineering simulations, physics, chemistry, statistics, machine learning, artificial intelligence, business logic, or objectives. These models can be displayed via ontology representations and taxonomy modeling in order to aid human understanding of the findings.
Linking , Rules , Workflows using RDF
The findings from digital twins can be linked to create an overview, such as by taking the findings of equipment twins and putting them into a production line twin, which can then inform a factory-scale digital twin. By using linked digital twins in this way it is possible to enable smart industrial applications for real-world operational developments and improvements. Digital Twin provides all parts of the business insight into how some product or system they're already using is working now, with reasoning, simulations along with the integrated view.
Some Industry wise uses ?
Manufacturing
Digital twins can make manufacturing more productive and streamlined while reducing throughput times.
Automotive
One example of where digital twins are used in the automotive industry is to gather and analyze operational data from a vehicle in order to assess its status in real-time and inform product improvements.
Retail
Outside of manufacturing and industry, a digital twin is used in the retail sector to model and augment the customer experience, whether at the level of a shopping center or for individual stores.
Healthcare
The medical sector has benefitted from digital twins in areas such as organ donation, surgery training, and de-risking of procedures. Systems have also modeled the flow of people through hospitals and tracked where infections may exist and who may be in danger through contact.
Pharma
Digital twin technology can be used to create a virtual model of a drug molecule, which can then be tested for efficacy and safety in various simulated scenarios. This can potentially speed up the drug development process and reduce the cost of clinical trials.
Telco
Digital twin technology can be used to create virtual replicas of the telecom network infrastructure, which can be used to simulate and optimize network design and planning. This can help telecom companies reduce the time and costs associated with physical experimentation, and also help to ensure that the network infrastructure is optimized for performance and efficiency.
Disaster management
Global climate change has had an impact across the world in recent years, yet digital twin can help to combat this by the informed creation of smarter infrastructures, emergency response plans and climate change monitoring.
Smart City Projects
The digital twin can also be used to help cities become more economically, environmentally, and socially sustainable. Virtual models can guide planning decisions and offer solutions to the many complex challenges faced by modern cities. For example, real-time responses to problems can be informed by real-time information from digital twins to allow assets such as hospitals to react to a crisis
Benefits & Industry impacts?
Common benefits include increased reliability and availability through monitoring and simulation to improve performance. They can also reduce the risk of accidents and unplanned downtime through failure, lower maintenance costs by predicting failure before it occurs, and ensure production goals are not impacted by scheduling maintenance, repair, and the ordering of replacement parts. Digital Twin can also offer continued improvements by analyzing customization models and ensuring product quality through performance testing in real time. Through the integration of technologies such as Enterprise systems, RDF, artificial intelligence, machine learning, and software analytics with graph database data, digital twin creates a simulation model that can update alongside or in lieu of a physical counterpart. This allows companies to assess an entirely computerized development cycle from design to deployment and even decommissioning. The digital twin is key to Industry employees who will able to monitor operations in real-time, providing prior alerts of possible failures and allowing for real-time performance optimization and assessment with minimal loss of productivity.